In the previous article, I explained the Publish–Subscribe pattern in NATS, which is great for broadcasting messages to many subscribers. But sometimes you need a different style: you want to send a message and get a response back. This is where the Request–Reply pattern comes in.
What is Request–Reply?
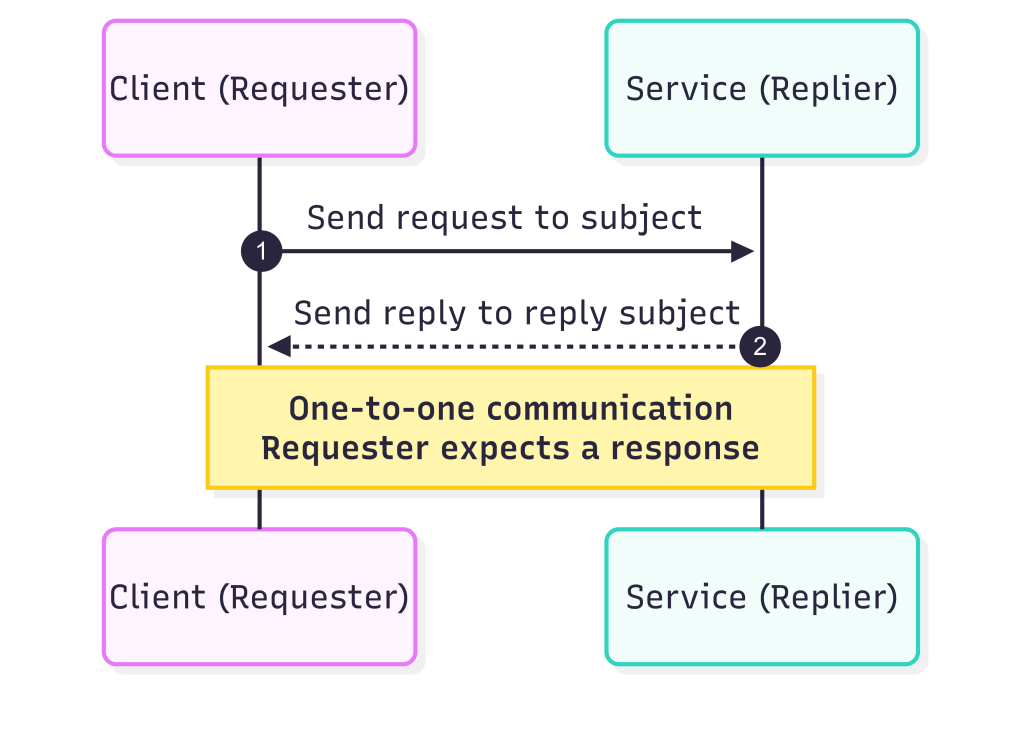
Request–Reply is a one-to-one communication pattern:
- A client (or requester) sends a request to a subject.
- A service (or replier) listens on that subject, processes the request, and sends back a response.
- The client waits for the reply, usually with a timeout.
Unlike pub/sub, where messages are broadcast to all subscribers, Request–Reply expects exactly one response.
Request–Reply in NATS
NATS makes this pattern very simple. The client uses the Request API, and the service uses a normal Subscribe.
Example in Go
Client (Requester):
msg, err := nc.Request("time.now", []byte(""), 2*time.Second)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Got reply: %s\n", string(msg.Data))
Service (Replier):
nc.Subscribe("time.now", func(m *nats.Msg) {
now := time.Now().Format(time.RFC3339)
m.Respond([]byte(now))
})
Here, the client sends a request to time.now. The service receives it and replies with the current time.
When to Use Request–Reply
- Querying a Service
- Example: A user profile service listens on
user.get. - A client sends a request with a user ID and gets back user details.
- Example: A user profile service listens on
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- You can design microservices where each service exposes a set of subjects.
- Other services can call them by sending requests.
- Health Checks
- Monitoring systems can send requests like
service.health. - Services reply with
"OK"or some status information.
- Monitoring systems can send requests like
Pages: 1 2
Category: NATS
