Example Use Cases with Subject Patterns
One of the strengths of NATS (and JetStream) is the subject pattern system. Subjects are like channels, and you can use wildcards to organize messages into logical groups. Here are some practical use cases:
1. Order Processing in E-Commerce
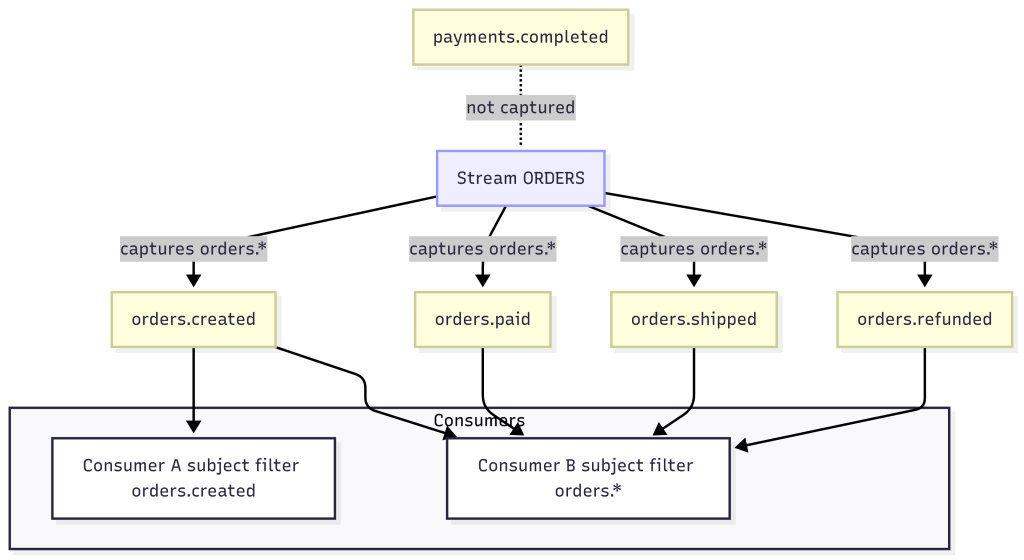
- Subjects:
orders.createdorders.paidorders.shipped
- How it works:
- A checkout service publishes to
orders.createdwhenever a new order is placed. - A payment service listens to
orders.created, processes payments, and publishes results toorders.paid. - A shipping service listens to
orders.paidand then sends messages toorders.shipped.
- A checkout service publishes to
- Why JetStream helps:
- Streams store all these messages.
- If the shipping service is down, when it comes back it can replay from where it left off.
- Developers can also replay the entire stream later to audit how an order moved through the system.
2. IoT Sensor Data
- Subjects:
sensors.building1.room23.temperaturesensors.building1.room23.humiditysensors.building2.room10.temperature
- Wildcard pattern:
sensors.*.*.temperature→ Subscribe to all temperature data across all buildings and rooms.sensors.building1.>→ Subscribe to all sensor data in building1.
- Why JetStream helps:
- Billions of sensor events can be persisted.
- Analytics services can replay old data for historical analysis.
- If a dashboard service is offline, it doesn’t lose data — it just replays from the stream.
3. Audit Logging for Compliance
- Subjects:
users.loginusers.logoutusers.failed_login
- How it works:
- Security services subscribe to all
users.*events. - If there’s a breach, investigators can replay all login attempts using JetStream.
- Security services subscribe to all
- Why JetStream helps:
- Keeps an immutable log of authentication events.
- Developers can configure the stream to keep data for 90 days or more.
4. Microservices with Event Sourcing
- Subjects:
inventory.item_addedinventory.item_removedinventory.stock_adjusted
- How it works:
- Inventory changes are always stored as events.
- A microservice can rebuild its state by replaying the event stream.
- Why JetStream helps:
- Reliable storage of all state changes.
- Easy to recover service state after a crash.
5. Multi-Tenant Applications
- Subjects:
tenantA.payments.completedtenantB.payments.completedtenantC.payments.completed
- Wildcard pattern:
*.payments.completed→ Subscribe to all tenants.tenantA.payments.*→ Subscribe only to tenant A’s payment events.
- Why JetStream helps:
- Each tenant’s events can be separated logically but still stored in a single stream.
- You can replay data per tenant for debugging or reporting.
Category: NATS
